Ubiquinol helps support optimal heart health
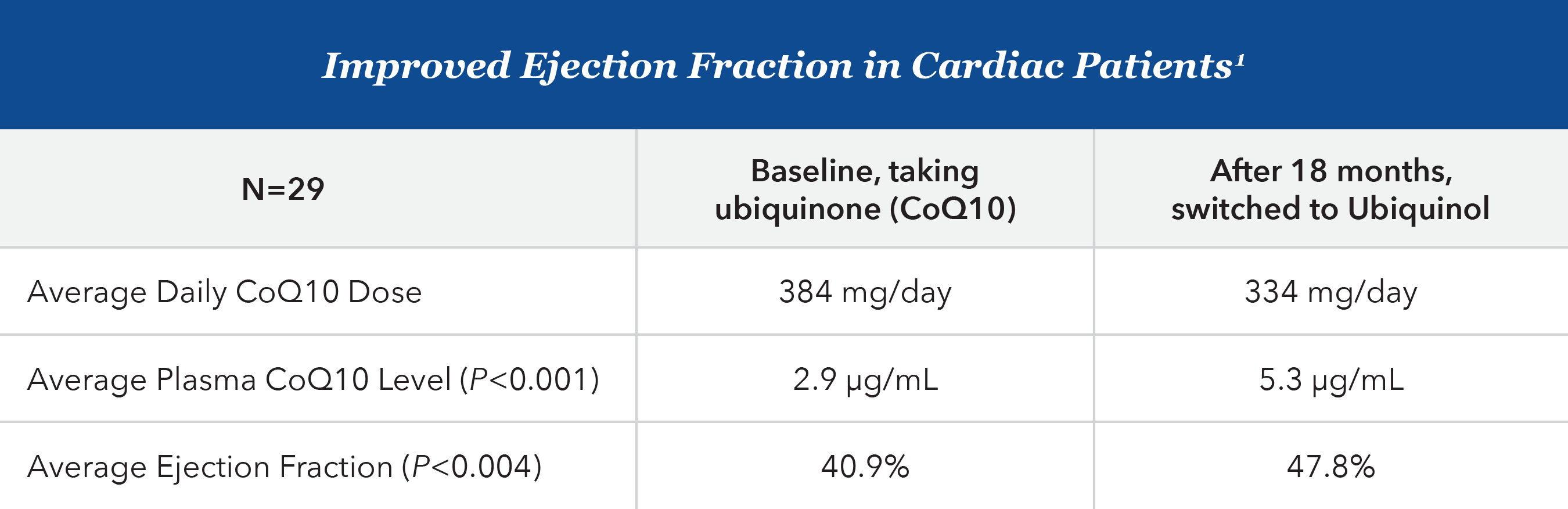
The role of Ubiquinol in restoring depleted levels of CoQ10 and improving ejection fraction1
-
In case reports of 29 cardiac patients, those patients who switched to Ubiquinol (average of 334 mg/day) from CoQ10 (average 384 mg/day) for 18 months experienced an increase in average serum CoQ10 level from 2.9 µg/mL to 5.3 µg/mL (P<0.001)1
- Average ejection fraction (EF), a measurement of the percentage of blood leaving (ejected from) the heart each time it contracts, improved from 40.9% to 47.8% (P<0.004)1
Higher Ubiquinol levels are shown to be associated with lower levels of blood markers of oxidative stress, including GGT, NT-proNBP, and CRP2-7
GGT (gamma glutamyltransferase)
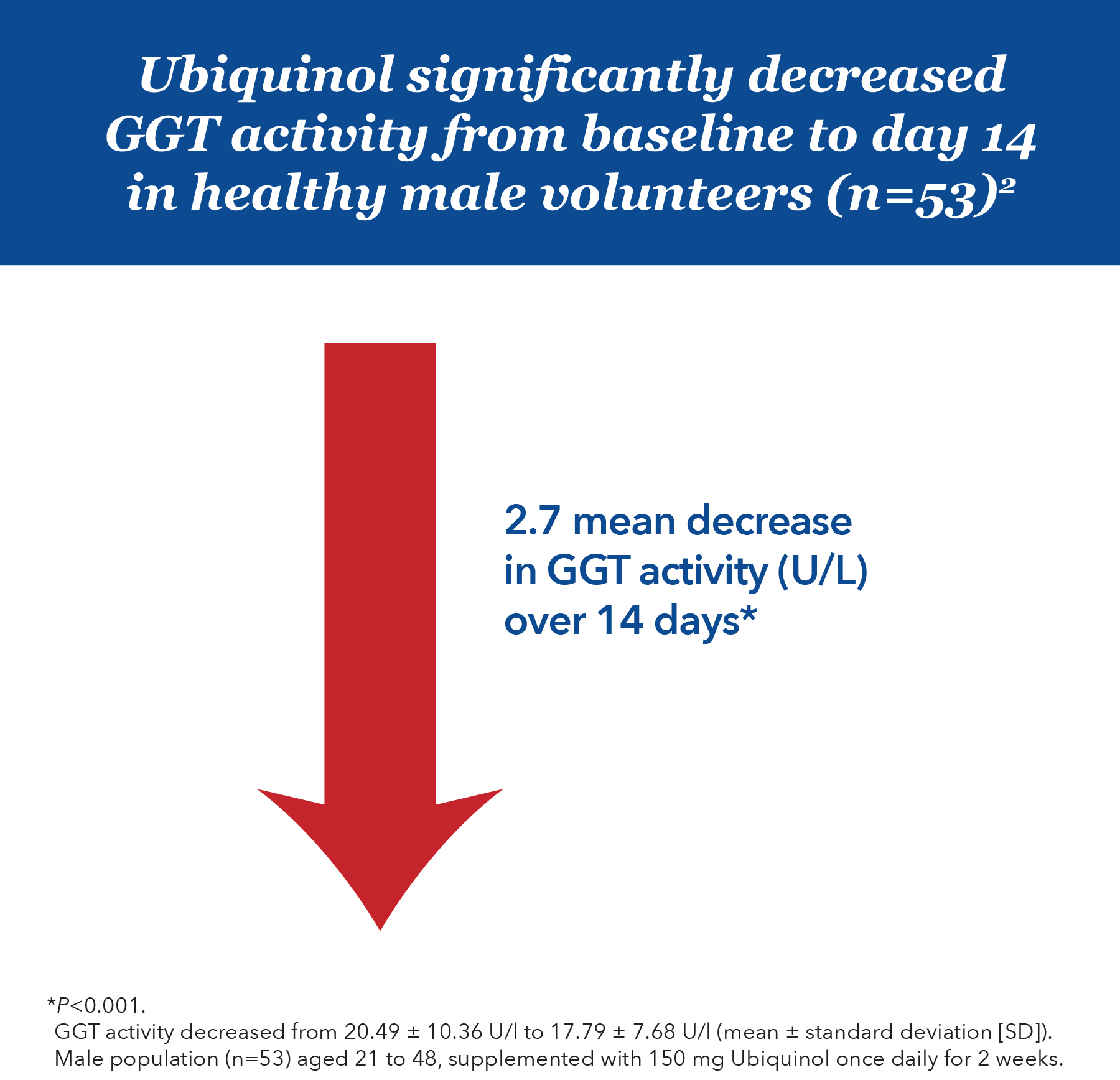
Ubiquinol reduces GGT in men2
- GGT is considered a marker of oxidative stress3
- Elevated serum GGT levels are associated with the development of certain cardiovascular conditions3-5
NT-proBNP
Higher serum levels of Ubiquinol, an antioxidant, are associated with lower serum NT-proBNP (N-terminal pro b-type natriuretic peptide) levels6
- Elevated values of NT-proBNP are associated with certain cardiovascular conditions6
- To read more about how Ubiquinol acts as an antioxidant, click here
C-reactive protein
The relationship between CoQ10 and the serum level of c-reactive protein (CRP) was investigated in a large study population (n=1319; patient mean age of 48.0 ± 14.4 years)7
- Ubiquinol status in plasma was significantly (P<0.001) correlated to the concentration of CRP; the greater the levels of oxidized CoQ10, the greater the levels of CRP7
- CRP in the blood may be a sign of a health condition
- In a follow-up study with 53 healthy male patients, daily supplementation with 150 mg of Ubiquinol for 14 days significantly increased Ubiquinol plasma concentrations and decreased the CoQ10 redox status (% of oxidized form of CoQ10)7
Additional evidence
As reported in a small pilot study, Ubiquinol was shown to improve endothelial function in cardiac patients with reduced ejection fraction8
- Ubiquinol 400 mg/day for 3 months provided significant improvement in peripheral endothelial function in patients with HFrEF (heart failure with reduced ejection fraction) as measured by reactive hyperemia index (RHI)
- RHI significantly improved with Ubiquinol (P=0.026) but not with placebo (P=0.198)
- Subjects: n=14; mean age 70; 86% male
- To read about a larger study where Ubiquinol significantly improved endothelial function in healthy patients with mild-to-moderate dyslipidemia, click here.
References
- Langsjoen PH, Langsjoen AM. Supplemental ubiquinol in congestive heart failure—3 year experience. Presented at: 6th International CoQ10 Association Conference; May 29, 2010; Brussels, Belgium.
- Onur S, et al. Ubiquinol reduces gamma glutamyltransferase as a marker of oxidative stress in humans. BMC Res Notes. 2014;7:427.
- Lee D-H, Jacobs DR, Gross M, et al. Y-glutamyltransferase is a predictor of incident diabetes and hypertension: the coronary artery risk development in young adults (CARDIA) study. Clin Chem. 2003;49(8):1358-1366.
- Jousilahti P, Rastenyte D, Tuomilehto J, et al. Serum gamma-glutamyl transferase, self-reported alcohol drinking, and the risk of stroke. Stroke. 2000;31:1851-1855.
- Dhingra R, Gona P, Wang T, et al. Serum γ-glutamyl transferase and risk of heart failure in the community. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010;30(9):1855-1860.
- Onur S, et al. Association between serum level of ubiquinol and NT-proBNP, a marker for chronic heart failure, in healthy elderly subjects. BioFactors. 2015;41(1):35-43.
- Fischer A, et al. Coenzyme Q10 redox state predicts the concentration of c-reactive protein in a large Caucasian cohort. BioFactors. 2016;42(3):268-276.
- Kawashima C, Matsuzawa Y, Konishi M, et al. Ubiquinol improves endothelial function in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a single-center, randomized double-blind placebo-controlled crossover pilot study. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2019. doi:10.3390/nu12041098.
Be a heart health INSIDER.
Sign up to receive news, updates and special offers on heart health and Ubiquinol.
Request patient samples of Ubiquinol.
Getting samples is easy—just fill out our online form.

