Ubiquinol improves arterial health to support blood circulation
Ubiquinol significantly improves endothelial function1
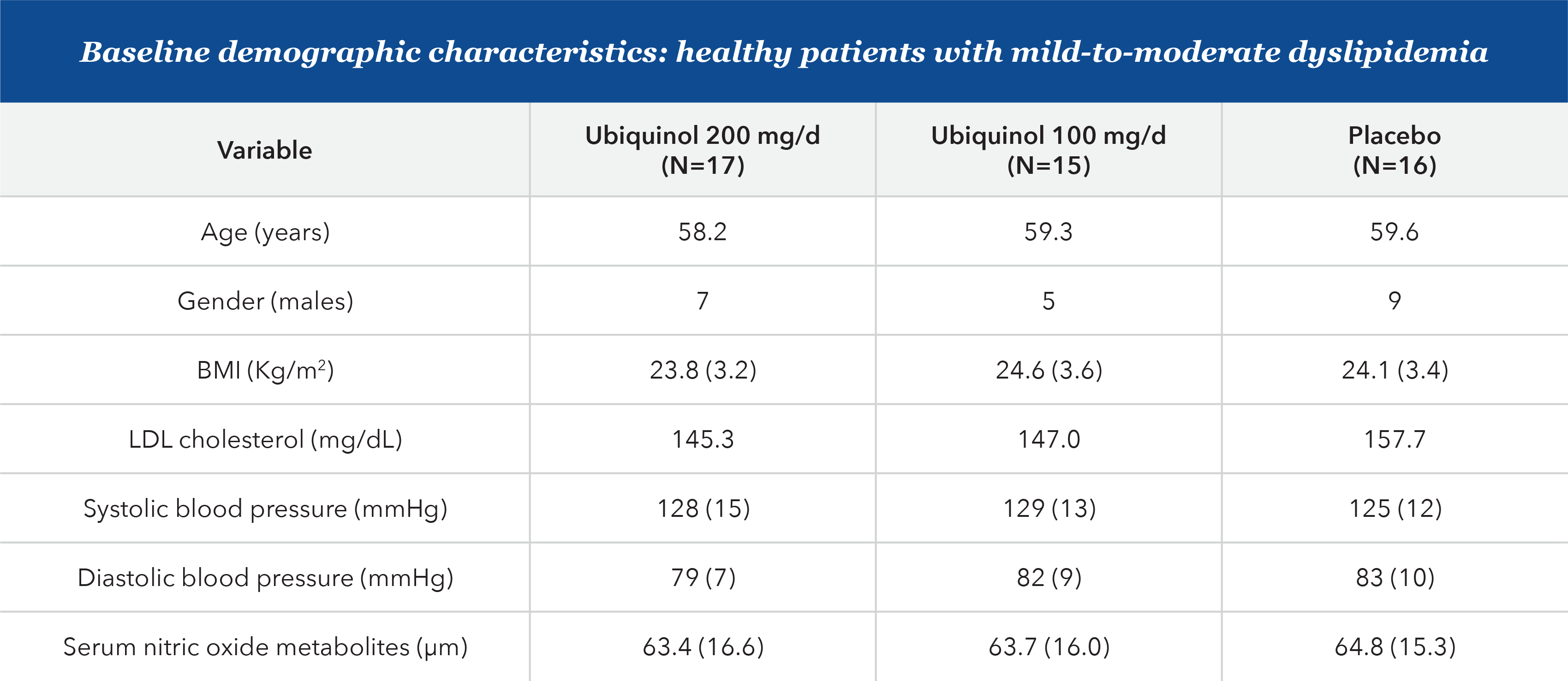
In an 8-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single-center trial, with the primary outcome of change in flow-mediated dilation (FMD) in healthy patients with mild-to-moderate dyslipidemia, Ubiquinol significantly improved dyslipidemia-related endothelial dysfunction (P=0.001).
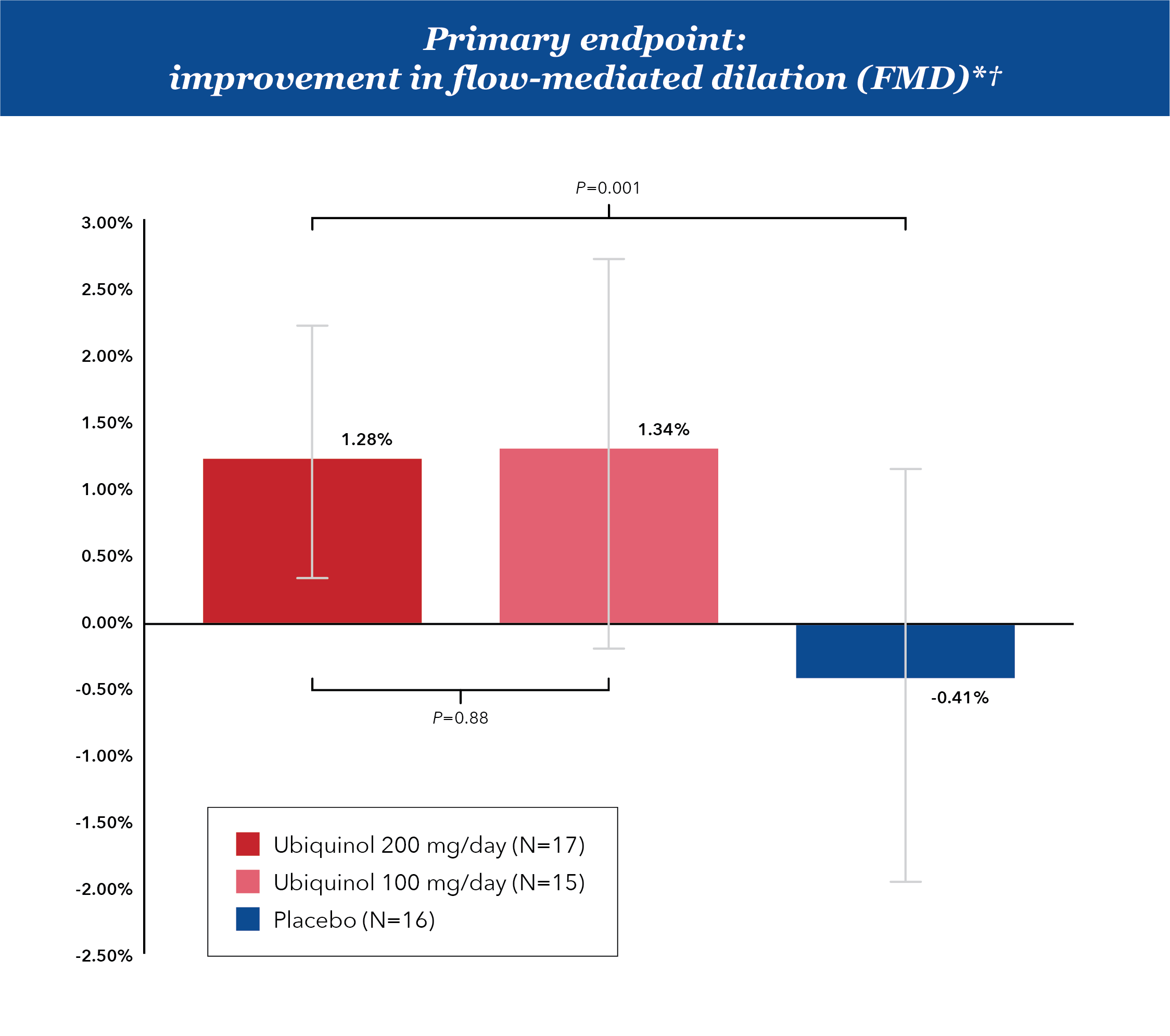
*Response with Ubiquinol was dose-independent.
†No significant changes in plasma lipid profile between groups or versus baseline for either group (one-way ANOVA, P=0.905). Ubiquinol improved endothelium-dependent vasodilation independent of plasma cholesterol levels.
Flow-mediated dilation refers to a measurement of change (widening) of brachial artery diameter following an induced increase in blood flow. FMD reflects nitric oxide-mediated arterial function, and is a measure of blood vessel health.
Cardiovascular health is associated with many factors, including diet, lifestyle and genetics. According to a 2019 expert consensus report, each 1% increase in FMD involves a significant 8% to 13% reduction in the risk of cardiovascular events.2
Significant improvements on 3 secondary endpoints
- Ubiquinol increased plasma CoQ10 levels versus placebo (P<0.001), and reduced the percentage of oxidized CoQ10 (P<0.001)
- Serum NOx increased significantly in all subjects receiving Ubiquinol (P=0.016) versus placebo
- Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) oxidation lag time improved significantly in those receiving 200 mg/day Ubiquinol (P=0.017) versus placebo
The improvement in endothelial function with Ubiquinol was positively correlated with increased NOx concentration (P=0.012) and increased LDL lag time over the course of the study (P=0.031).
Safety profile
No adverse events were reported.
An 8-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
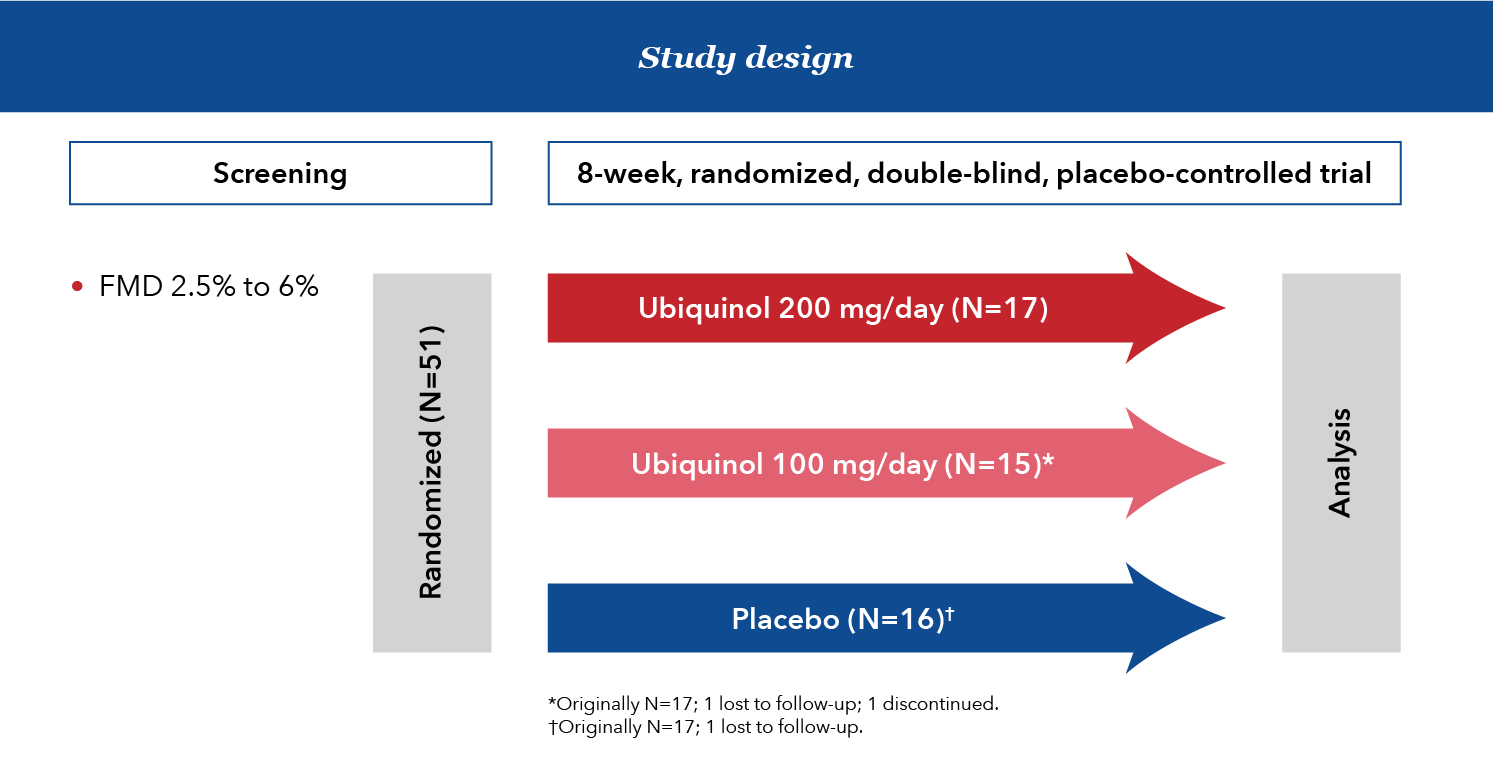
Patients were healthy with mild-to-moderate dyslipidemia
Ubiquinol significantly improved endothelial function in cardiac patients with reduced ejection fraction3
In a separate small, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study of 14 patients with HFrEF (heart failure with reduced ejection fraction), Ubiquinol 400 mg/day for 3 months provided significant improvement in peripheral endothelial function.
- Peripheral endothelial function was assessed using the reactive hyperemia index (RHI)
- RHI significantly improved with Ubiquinol (P=0.026) but not with placebo (P=0.198)
References
- Sabbatinelli J, Orlando P, Galeazzi R, et al. Ubiquinol ameliorates endothelial dysfunction in subjects with mild-to-moderate dyslipidemia: a randomized clinical trial. Nutrients. 2020;12(4):1098. doi:10.3390/nu12041098.
- Thijssen DHJ, Bruno RM, van Mil A, et al. Expert consensus and evidence-based recommendations for the assessment of flow-mediated dilation in humans. Eur Heart J. 2019;40:2534-2547. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehz350.
- Kawashima C, Matsuzawa Y, Konishi M, et al. Ubiquinol improves endothelial function in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a single-center, randomized double-blind placebo-controlled crossover pilot study. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2020;20:363-371. doi:10.1007/s40256-019-00384-y.
Be a heart health INSIDER.
Sign up to receive news, updates and special offers on heart health and Ubiquinol.
Request patient samples of Ubiquinol.
Getting samples is easy—just fill out our online form.

