
What is Ubiquinol & What Does It Do?
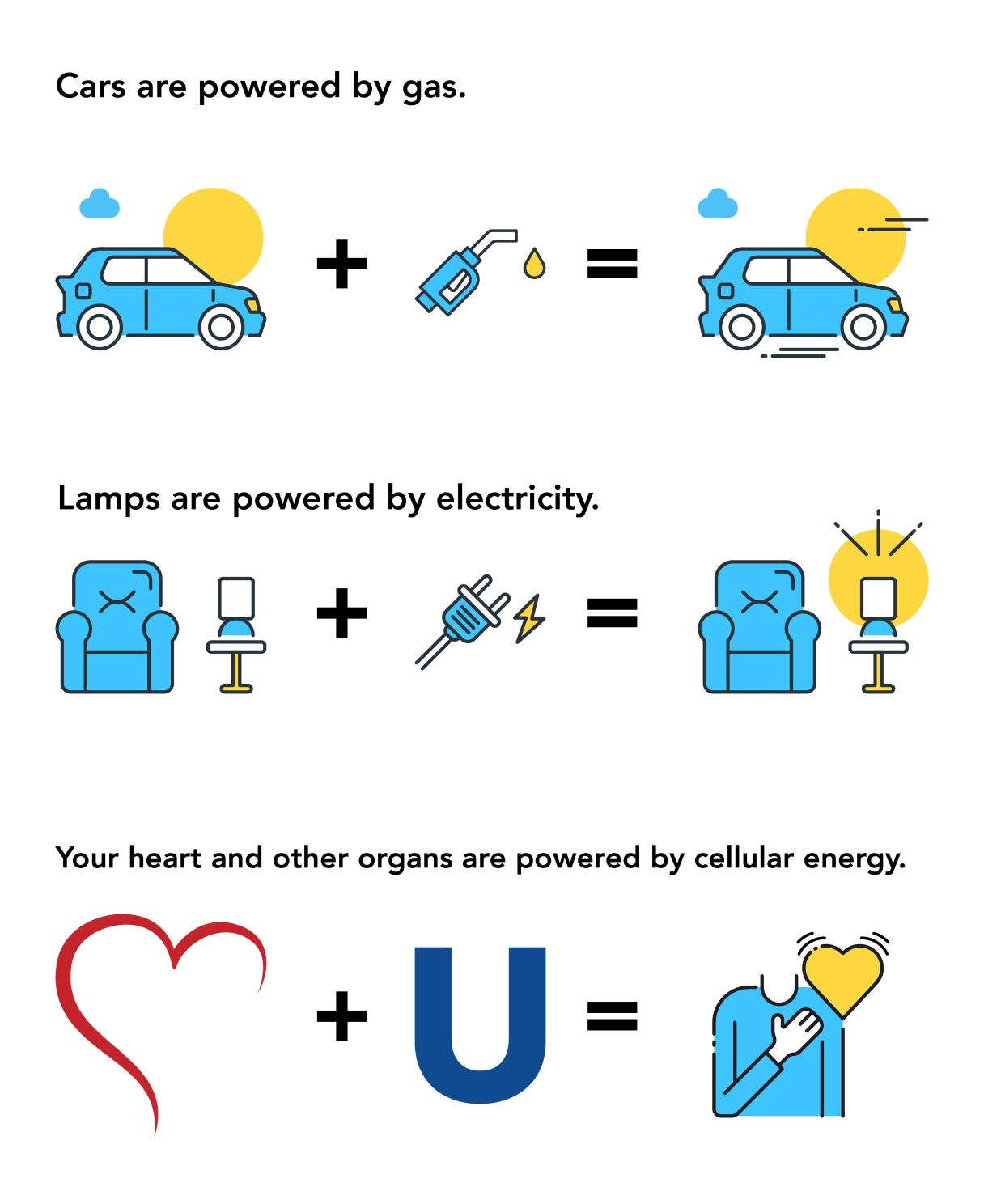
Ubiquinol is the active form of CoQ10 and plays a key role in producing the cellular energy your organs need to keep functioning - for example, cellular energy is what makes your heart pump. A lamp is powered by electricity. A car is powered by gas. Your heart and other organs are powered by cellular energy.
Benefits of The Ubiquinol Form of CoQ10
CoQ10 has interested researchers for many years, but the Ubiquinol form of CoQ10 has been commercially available in America for only 12 years. In that short time, more than 60 peer-reviewed clinical and research studies have been performed and over 1,800 scientific papers have been published regarding Ubiquinol, and its health benefits.
This large and still growing amount of research has found that the Ubiquinol form of CoQ10:
- Supports optimal heart health1 2 3
- Supports the body's cellular energy production4
- Helps prevent damage in the body caused by oxidative stress5
- Replenishes CoQ10 blood levels depleted by statin cholesterol medicines6 7
- Is a powerful antioxidant that helps neutralize free radicals that may otherwise damage healthy cells in the body8
LEARN MORE: Find out more about Ubiquinol as an antioxidant
Ubiquinol is a vitamin-like substance that’s naturally made in our bodies and plays a critical role in the creation of cellular energy. We make less of the heart-healthy nutrient starting around age 40
Ubiquinol as an Antioxidant
Unlike conventional CoQ10, Ubiquinol is also a very powerful antioxidant thanks to its extra electrons. Those electrons hold the key to neutralizing substances called free radicals.
Free radicals are harmful because they are constantly looking to steal electrons wherever they may be found, including DNA, proteins and lipids. Removing an electron oxidizes the molecule (known as oxidative stress) and can cause damage that impacts our health.
The Ubiquinol form of CoQ10 doesn’t mind giving up an electron to neutralize a free radical that might have otherwise caused oxidative stress.
What’s more, Ubiquinol is one of the few antioxidants that work both in the fatty parts of our body (such as cell membranes and LDL cholesterol) and also in the mitochondria where energy is manufactured. Like car engines produce exhaust, the mitochondria have their own form of exhaust filled with free radicals.
Ubiquinol is the only form of CoQ10 capable of protecting the mitochondria and their lipid membranes from free radical attack.
In addition to these benefits, researchers from around the world are busy studying the role Ubiquinol may play in mitochondrial function, brain health, vision health and bone metabolism, among other areas.
Before it can do many of the wonderful things people associate with this nutrient, our bodies need to convert the conventional form of CoQ10 into Ubiquinol.
Types of CoQ10
CoQ10, or Coenzyme Q10, is one of America’s most recognized supplements. Although millions of us buy the supplement to support heart health, most people don’t know there are two forms of this nutrient: Ubiquinone and Ubiquinol. Each exist naturally in the body, but function differently.
Ubiquinol, sometimes called the advanced or active form of CoQ10, is the predominant form of CoQ10 in a healthy young adult2 4 9. Ubiquinone, the conventional form of CoQ10, must be converted into Ubiquinol to create cellular energy. However, as you age, your body’s ability to convert Ubiquinone into Ubiquinol decreases.10 11
Discover the differences between Ubiquinone and Ubiquinol now
Why Take The Ubiquinol Form Of CoQ10
When comparing Ubiquinol to conventional CoQ10, the published studies to date indicate that Ubiquinol is better absorbed by the body.12 13 14 The amount your body absorbs will vary based on your age and overall health, but studies have consistently shown Ubiquinol to be the easiest form of CoQ10 for your body to use.
Turning conventional CoQ10 into Ubiquinol becomes harder and less efficient as we age, which is why “older” adults who take a CoQ10 supplement would be wise to choose Ubiquinol.
**All of our Kaneka Ubiquinol is made directly in the USA at our plant in Pasadena, TX**
Are you taking the right form of CoQ10?
Ubiquinol vs. CoQ10
Get your FREE Beginner's Guide To Ubiquinol
References
2 Langsjoen PH and Langsjoen AM. Supplemental Ubiquinol in congestive heart failure: 3 year experience. 6th International Q10 Conference Brussels, 27–30 May 2010; 29–30.
4 Becker WM and Deamer DW. Energy from Chemical Bonds: The aerobic mode. In: The World of the Cell, 2nd Ed., The Benjamin Cummings Publishing Company, Inc, Redwood City , CA., pps. 275-313.




