
CoQ10, Ubiquinol, and Statins
If you have high cholesterol, your doctor may prescribe a statin, a cholesterol-lowering drug. While statins are effective in lowering cholesterol levels, many people don’t know that they also lower the body’s natural production of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) — a naturally occurring nutrient in your body. Lowered production of CoQ10 can lead to less Ubiquinol in the blood and tissues. Ubiquinol is the antioxidant form of CoQ10 and it plays an essential role in creating cellular energy that helps fuel your heart and other organs. Even small decreases in Ubiquinol can disrupt the body’s ability to produce cellular energy and lead to oxidative stress, which is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in your body that can cause damage to organs and tissues.
READ MORE: What’s the Difference Between Ubiquinol and Ubiquinone?
Reduced levels of Ubiquinol can also affect your low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, also known as “bad” cholesterol. As the body’s strongest fat-soluble antioxidant, Ubiquinol can help defend against the oxidation of LDL cholesterol by inactivating free radicals. With lowered CoQ10 levels, LDL cholesterol can become more susceptible to oxidation and free radical damage which can impact vascular health. Watch the video below to learn more about why taking a Ubiquinol supplement with a statin is vital for maintaining healthy Ubiquinol CoQ10 levels and supporting your heart’s health.
So, if you’re taking statins, you might consider taking a Ubiquinol supplement. Let’s take a closer look at CoQ10 and statin drugs.
CoQ10, Ubiquinol, and Statins
Statin drugs (Lipitor®, Zocor®, Pravachol®, Crestor®, and the like) are prescribed to lower a person's cholesterol level. They do this by inhibiting the body's internal production of cholesterol . At the same time, these drugs inhibit the body's production of CoQ10.1 3 4 This means there is less CoQ10 — and ultimately less Ubiquinol — in the blood, particularly in people who have been on statins at high doses or for a long time.
Why Do People Take Ubiquinol With Statins?
The Connection Between CoQ10 and Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a naturally occurring substance that’s found in every cell of your body and plays an important role in making hormones and vitamin D and supporting digestion. However, too much cholesterol can cause health problems. If you have high cholesterol, your doctor may prescribe a statin for you. That’s great for lowering cholesterol, but it’s also important to be aware that statins can impact your CoQ10 levels.
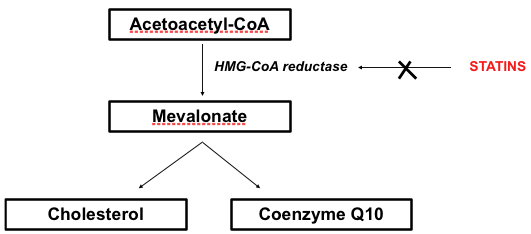
The key is that both cholesterol and CoQ10 are produced in the body through the same pathway. As you can see in the figure below, acetoacetyl-CoA gets changed into mevalonate. This is done with the help of the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase. Mevalonate can then be used to make either cholesterol or CoQ10. This is called the “mevalonate pathway” and we've simplified several steps in between for clarity.
Statins work by inhibiting the action of HMG-CoA reductase so that the amount of mevalonate formed is decreased. With less mevalonate, less cholesterol is formed, and this is exactly what you want to have happen when your cholesterol is too high. However, in doing so, the amount of CoQ10 that the body makes is also decreased. And, lower CoQ10 levels can lead to less Ubiquinol in your body.
Ubiquinol and Statin Research
Studies have shown that Ubiquinol effectively restores the CoQ10 that statins can deplete over time. Research also shows that when compared to conventional CoQ10, Ubiquinol is better able to replenish CoQ10 levels in statin users.
On a Statin? Here’s Why Ubiquinol is an Important Supplement.
If you’re prescribed a statin, this may decrease your natural blood levels of CoQ10 and with it Ubiquinol.3,4 Maintaining a healthy Ubiquinol/CoQ10 balance in the body is especially important -if taking a statin, and as we age. While Ubiquinol is the predominant form of CoQ10 in healthy people, due to aging and other lifestyle factors such as unhealthy diets and high stress levels, the proportion of Ubiquinol can fall below ideal levels.
Why does this matter so much? Here are two important reasons for choosing a Ubiquinol supplement:
1. Ubiquinol is Better Absorbed than Conventional CoQ10
In a healthy adult, 95% or more of the total CoQ10 in the body is in the Ubiquinol form, with the greatest concentration in the heart and other organs with high energy demands such as the kidneys and liver. Ubiquinol has been shown to be 2-4x better absorbed than conventional CoQ10. Supplementing with Ubiquinol provides the already activated, antioxidant form of CoQ10, facilitating its functionality in the blood and tissues. Studies have shown that Ubiquinol supplementation improved certain blood markers associated with heart health including LDL oxidation and nitric oxide production.
2. Ubiquinol Is A Powerful Antioxidant
Oxidative stress is when we have an imbalance between the antioxidants and free radicals in our bodies. Although mild, short-term oxidative stress is nothing to worry about, long-term oxidative stress can damage the body’s cells and contribute to premature aging and the development of chronic health conditions.
If you have been prescribed a statin, there are many good reasons to add a Ubiquinol supplement to your daily routine, and make sure the dietary supplement label says “Kaneka Ubiquinol®.”
Final Thoughts on Ubiquinol Supplements & Statins
If you have high cholesterol and your doctor prescribes you a statin, that’s great news for lowering your cholesterol. It is important to keep in mind that a statin can also lower your CoQ10 levels, in turn reducing the Ubiquinol in your blood. Ubiquinol is important in creating cellular energy that helps fuel your heart and other organs. However, as mentioned, even small decreases in Ubiquinol can disrupt the body’s ability to produce energy and lead to oxidative stress. That’s why taking a Ubiquinol supplement can be especially beneficial if you’re taking a statin.
As always, if you are taking a statin or other prescription medication, we encourage you to speak with your doctor before taking a new supplement like Ubiquinol.
|
Conventional CoQ10 is a good option for: Young people under 40 |
The Ubiquinol form of CoQ10 is a good option for: Anyone over 40 and those taking statins |
Why?
|
Why?
|
Are you combatting the side effects of statins?
Get the Heart-Health E-book
References
3 Mortensen SA, Leth A, Agner E, Rohde M. Dose-related decrease of serum coenzyme Q10 during treatment with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Mol Aspects Med Suppl 1997;18: S137–144.
4 Watts GF, Castellucci C, Rice-Evans C et al., Plasma coenzyme Q (ubiquinone) concentrations in patients treated with simvastatin. J. Clin Pathol. 1993;46(11):1055–1057.
7 Forsmark-Andrée P, Ernster L. Evidence for a protective effect of endogenous ubiquinol against oxidative damage to mitochondrial protein and DNA during lipid peroxidation. Mol Aspects Med. 1994;15 Suppl:s73-81




